Hindu Philosophy foundations and types of schools
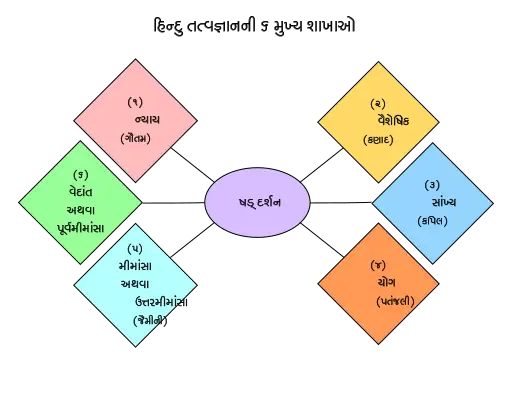
Hindu philosophy schools are known as Darshanas. There are six orthodox (āstika) schools of thought, which accept the authority of the Vedas:
- Samkhya is a dualistic school of Hindu Philosophy thought that propounds the existence of two ultimate realities: Purusha (consciousness) and Prakriti (matter).
- Yoga is a practical school of thought that emphasizes the use of meditation and other yogic practices to achieve liberation from the cycle of birth and death.
- Nyaya is a school of logic and epistemology that is concerned with the nature of knowledge and how to acquire it.
- Vaisheshika Hindu Philosophy is a school of realism that is concerned with the nature of reality and its constituents.
- Purva Mimamsa is a school of ritualism that is concerned with the interpretation and performance of Vedic rituals.
- Uttara Mimamsa (Vedanta) is a monistic school of thought that propounds the existence of one ultimate reality, Brahman.
Each of these schools of thought has its own unique perspective on the nature of reality, the meaning of life, and the path to liberation. They have also had a profound influence on Indian culture and thought, and continue to be studied and debated by scholars today.
In addition to the six orthodox schools, there are also five heterodox (nāstika) schools of thought, which do not accept the authority of the Vedas:
These schools of thought have their own unique philosophical perspectives, which often differ significantly from those of the orthodox schools.
Hindu philosophical schools are a diverse and complex tradition, but they all share a common goal: to understand the nature of reality and to achieve liberation from the cycle of birth and death.
Image credit
Mrigiya, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons