Keywords of AI & LLMs
Understanding keywords related to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for grasping their functionality, applications, and development. Here are some essential keywords and concepts:
- Large Language Models (LLMs):
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): A type of LLM developed by OpenAI, known for its ability to generate human-like text.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): An LLM developed by Google, designed to understand the context of words in search queries.
- Transformer: The neural network architecture that underpins most modern LLMs, including GPT and BERT, known for its efficiency in handling sequential data like text.
- Training:
- Pre-training: The initial phase where the model learns from a large corpus of text data in an unsupervised manner.
- Fine-tuning: Adjusting a pre-trained model on a smaller, task-specific dataset to improve performance on that specific task.
- Backpropagation: The process of adjusting the weights of a neural network based on the error rate of the output compared to the expected outcome.
- Architecture:
- Neural Networks: Computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks of animal brains, essential for learning patterns in data.
- Attention Mechanism: A component of the Transformer architecture that allows the model to focus on relevant parts of the input when generating an output.
- Parameters: The weights and biases in a neural network that are learned from the training data and used to make predictions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Tokenization: Breaking down text into smaller units like words or subwords that the model can process.
- Embedding: Representing words or tokens as vectors in a continuous vector space.
- Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq): A model architecture used for tasks where the input and output are both sequences, such as translation.
- Applications:
- Chatbots: AI systems designed to simulate conversation with human users.
- Text Generation: The creation of new text based on a given input, used in applications like story writing or code generation.
- Machine Translation: Automatically translating text from one language to another.
- Ethics and Bias:
- Bias: The tendency of an AI system to make decisions based on prejudiced or unbalanced data.
- Fairness: Ensuring AI systems make impartial and just decisions.
- Explainability: The ability to explain how an AI model arrives at a decision, which is critical for trust and transparency.
- Evaluation:
- Perplexity: A measure of how well a language model predicts a sample; lower perplexity indicates better performance.
- BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy): A metric for evaluating the quality of text which has been machine-translated from one language to another.
- Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1 Score: Standard metrics for evaluating the performance of classification models.
Understanding these keywords provides a solid foundation for diving deeper into the field of AI and LLMs, enabling a better grasp of both the theoretical and practical aspects of these technologies.
Image credit
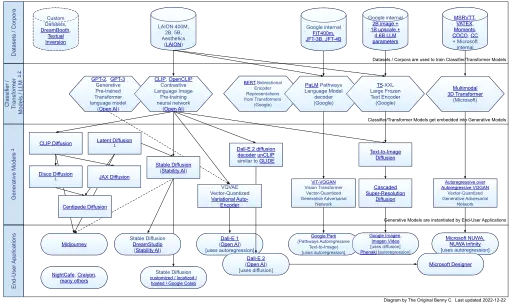
The Original Benny C, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons